Understanding Ihm Scada Systems
This article delves into the realm of Ihm Scada systems, highlighting their significance in industrial automation. Ihm Scada, an integration of Interface Human Machine (IHM) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA), facilitates efficient monitoring and control over industrial processes. Its application spans various sectors, enhancing operational productivity through real-time data collection and analysis.
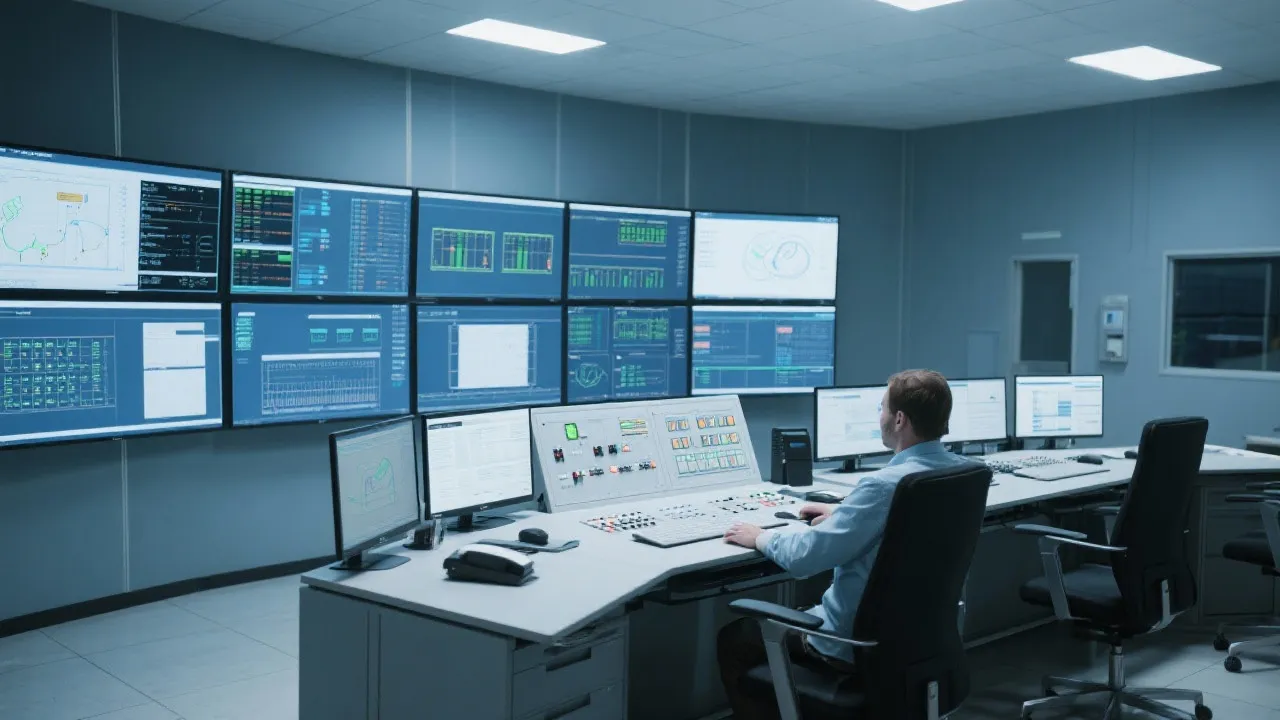

Introduction to Ihm Scada Systems
The convergence of Interface Human Machine (IHM) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems represents a pivotal advancement in industrial automation. Combining real-time data processing with user-friendly interfaces, Ihm Scada systems are indispensable for industries seeking optimal process management and operational efficiency. This article explores the multifaceted role of Ihm Scada in modern industrial frameworks, emphasizing its capabilities and applications, as well as the driving forces behind its adoption, and considerations for implementation and maintenance.
The Evolution of Industrial Automation
To truly appreciate the significance of Ihm Scada systems, one must understand the evolution of industrial automation itself. Early automation systems were mechanical, relying heavily on physical levers and manual adjustments. As industries grew increasingly complex, the need for more sophisticated control systems became evident. The advent of electronic control systems marked a significant shift, advancing toward programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that allowed for more complex operations efficiently. However, it was the integration of HMIs and SCADA systems that heralded a new era, enabling operators not only to control systems but also to visualize processes in real-time, analyze data thoroughly, and automate significant portions of operations.
Core Components of Ihm Scada
Ihm Scada systems are comprised of several essential components, each playing a critical role in the seamless management of industrial operations:
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): The graphical interface through which operators interact with the system, providing control and monitoring capabilities. HMIs can vary greatly in design, ranging from simple LCD displays to advanced touch-screen interfaces with detailed graphical representations of the plant floor.
- Supervisory Control System: A high-level system that oversees processes, providing data collection, and facilitating decision-making. The supervisory system orchestrates the entire operation, ensuring that all components function harmoniously.
- Data Acquisition System: Collects and transmits data from various sensors and devices within the industrial setting for processing and analysis. This system is vital for turning raw data into actionable information that can drive operational improvements.
- Remote Terminal Units (RTUs): Field devices that interface with sensors and actuators, transmitting data to the central SCADA unit. RTUs play a critical role in remote monitoring and control, bridging the gap between physical equipment and the supervisory system.
Application Across Industries
The implementation of Ihm Scada systems transcends multiple industries, each leveraging its capabilities to achieve distinct operational goals:
- Manufacturing: Ihm Scada systems facilitate real-time monitoring of production processes, improving throughput and reducing downtime. Manufacturers can utilize these systems for predictive maintenance, minimizing the chances of unexpected failures that can halt production lines.
- Energy Management: Enhances efficiency in the distribution and utilization of energy resources across vast networks. With the growing importance of renewable energy, Ihm Scada systems are crucial in managing energy flows between different sources and consumers, ensuring stability in the grid.
- Water and Waste Management: Optimizes the control of complex distribution systems and wastewater treatment processes. These systems monitor water quality and flow rates, ensuring compliance with environmental standards and promoting sustainable practices.
- Telecommunications: Ensures seamless network management through effective data handling and resource allocation. In this sector, Ihm Scada systems can oversee the operational status of communication networks, allowing companies to prevent outages and maintain service continuity.
- Pharmaceuticals: Leverages Ihm Scada systems for strict compliance with regulations, ensuring that production processes meet safety and quality standards. Monitoring conditions such as temperature and humidity in real-time is essential for maintaining the integrity of sensitive products.
Advantages of Ihm Scada Systems
Adopting Ihm Scada systems offers a range of advantages that significantly enhance operational effectiveness:
- Improved Decision-Making: With access to real-time data, operators can make informed decisions swiftly. Insights derived from analytics provide managers with a foundation for strategic planning and operational improvements.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency: Streamlining processes leads to reduced wastage and increased productivity. The automation of routine tasks allows personnel to focus on higher-level functions, ultimately leading to better resource utilization.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Systems can be tailored to meet specific industrial needs and scaled as operations grow. Businesses can adapt their SCADA systems to evolving technologies, such as IoT integration, ensuring longevity and relevance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces labor costs by automating routine tasks and minimizing errors. Additionally, by improving operational efficiency, companies can achieve cost savings that positively impact their bottom line.
- Enhanced Safety: Ihm Scada systems contribute to workplace safety. By monitoring equipment performance and environmental conditions, the system can alert operators to potential hazards, enabling preventative measures to be taken in a timely manner.
Comparison of Ihm and SCADA Systems
| Feature | Interface Human Machine (IHM) | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Operator interface to control and monitor machinery | Comprehensive system for data collection and management |
| Data Handling | Real-time data presentation to operators | Data acquisition from multiple sources for analysis |
| Application | Primarily used for direct control and management by operators | Used for large-scale monitoring and analysis of industrial processes |
| System Priority | Focus on user experience and operator interaction | Focus on data integrity and system performance |
| Complexity | Generally simpler, requiring less training for operators | More complex, requiring comprehensive training for full efficacy |
Challenges in IHM SCADA Implementation
Despite the myriad of advantages, implementing Ihm Scada systems is not without its challenges. Organizations must navigate several hurdles to achieve smooth integration:
- Cost of Implementation: The initial investment for Ihm Scada systems can be substantial. This includes the cost of hardware, software, and training personnel. Some organizations may hesitate to adopt these systems due to budget constraints.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many industries operate with legacy systems that may not readily support modern Ihm Scada technologies. Bridging the gap between old and new technologies can be technically challenging and time-consuming.
- Data Security Concerns: The increase in cyber threats calls for rigorous cybersecurity measures. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring system integrity is a critical consideration when deploying Ihm Scada systems.
- Training and Skill Development: Users must be adequately trained to understand and utilize the full potential of Ihm Scada systems. This requires time and resources to ensure operators are confident and competent in their usage.
- Change Management: Transitioning to an Ihm Scada system requires significant adjustments to existing workflows. Resistance to change among employees can impact productivity and the success of implementation.
Best Practices for Ihm Scada Deployment
To overcome challenges associated with Ihm Scada system implementation, organizations can adopt several best practices:
- Conducting a Thorough Needs Assessment: Understand the specific requirements and goals of the organization before choosing or customizing an Ihm Scada system. This ensures that the chosen solution aligns with operational objectives and addresses unique challenges faced by the business.
- Phased Implementation: Instead of a full-scale rollout, consider a phased approach that allows for gradual integration. This can help alleviate resistance to change, identify any issues early, and provide time for staff to adapt to the new system.
- Prioritizing Training Programs: Invest in comprehensive training programs that cater to different user groups. This will ensure that all operators, management, and maintenance personnel understand how to use the system effectively and can leverage its features for improved performance.
- Establishing a Support Framework: Create a structure that provides ongoing technical and operational support post-deployment. This includes having experts available to assist with troubleshooting and optimization as users become accustomed to the new system.
- Regular Monitoring and Updates: Conduct regular evaluations of the system’s performance and gather feedback from users. This can lead to meaningful improvements and updates, ensuring that the system continues to meet the organization’s evolving needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What industries benefit very from Ihm Scada systems?
Industries such as manufacturing, energy, water and waste management, and telecommunications benefit significantly from Ihm Scada systems due to their need for real-time monitoring and control. Furthermore, sectors like pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and transportation are increasingly adopting these systems to enhance operational safety and efficiency.
How does Ihm Scada improve operational efficiency?
Ihm Scada enhances efficiency through automated process control, real-time monitoring, detailed analytics, and quick decision-making, which collectively minimize downtime and optimize resource use. These capabilities allow organizations to make data-driven adjustments that result in smoother operations and reduced overhead.
Can Ihm Scada systems be customized?
Yes, Ihm Scada systems are customizable to meet specific operational requirements and can be scaled to accommodate business growth. Tailoring these systems ensures that they effectively address unique challenges specific to each industry or organization.
What are the future trends for Ihm Scada technology?
Future trends for Ihm Scada include increased integration with the Internet of Things (IoT), more advanced data analytics, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and greater user interface improvements to accommodate evolving industrial needs. Additionally, AI-driven analytics and machine learning are expected to reshape the decision-making process in real-time, providing even deeper insights for operational improvements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Ihm Scada systems stand as a testament to the progressive trajectory of industrial automation. Their ability to seamlessly integrate user interfaces with complex data processes ensures operational excellence across various industries. As technology continues to evolve, Ihm Scada systems will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of industrial process management. Furthermore, as industries face increasing pressures for sustainability, efficiency, and safety, the role of Ihm Scada systems will only grow, supporting organizations in navigating the complexities of modern operations.
Future Directions and Innovation in Ihm Scada Systems
The landscape of Ihm Scada systems is poised for significant transformation in the coming years as innovation continues to redefine industrial automation. Key areas of focus include:
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: As industries generate more data than ever before, the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms into Ihm Scada systems will enable smarter decision-making. Predictive analytics can spot trends and anomalies in real time, facilitating preventative maintenance and reducing operational risks.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Protocols: With the rise in cyber threats, there is a growing need for advanced security measures to protect Ihm Scada systems. Future innovations will focus on developing robust protocols that can safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
- Further Development of User Interfaces: Future trends will see the evolution of more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, employing augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies to offer operators immersive experiences that enhance understanding and control of complex systems. These technologies will not only improve training efficiency but also enable operators to visualize data more effectively.
- Data Accessibility via Cloud Computing: The cloud computing revolution opens new avenues for data storage and access. Cloud integration will enhance the accessibility of vital data from anywhere, allowing improved collaboration and communication across teams and locations.
- Sustainability Considerations: With a growing emphasis on sustainability, Ihm Scada systems will increasingly support initiatives geared toward reducing carbon footprints and optimizing resource use. This could involve developed functionalities that help organizations track their sustainability goals, enhancing their overall environmental performance.
Case Studies of Successful Ihm Scada Implementations
Examining real-world applications of Ihm Scada systems provides valuable insights into their effectiveness across various industries. Here are a few notable case studies:
1. Manufacturing - Automotive Industry
A large automotive manufacturer faced significant challenges related to production downtime and material wastage. By implementing an Ihm Scada system, they gained real-time visibility into production line processes. Operators could monitor machine performance and diagnose issues immediately, resulting in a 30% decrease in downtime and a 20% reduction in waste. The system's advanced analytics capabilities enabled the manufacturer to forecast maintenance needs, ensuring that machines were serviced proactively.
2. Energy Distribution
An electricity utility company adopted an Ihm Scada solution to manage its vast network more effectively. The new system provided real-time data on grid performance, allowing operators to respond quickly to outages and redistribute energy sources during peak demand. Over time, the utility experienced a 15% improvement in overall energy efficiency and boosted customer satisfaction due to fewer outages and faster response times.
3. Water Treatment Facilities
A municipal water treatment facility implemented Ihm Scada technology to enhance its distribution operations. The system monitored water quality and flow rates, automating adjustments to maintain regulatory compliance. With clearer insights into operation metrics, the facility reported a reduction in chemical usage by 25% while maintaining water safety standards. Furthermore, the ability to predict potential leaks led to improved resource management, ultimately lowering operational costs.
4. Pharmaceuticals and Biotech
A biotech company engaged in producing biopharmaceuticals required stringent control over its manufacturing processes due to strict regulatory requirements. The implementation of an Ihm Scada system enabled them to manipulate and monitor sensitive parameters in real-time. By achieving 100% visibility and control over their processes, the company significantly improved batch consistency and reduced the risk of contamination, contributing to the successful launch of new products.
5. Telecommunications Network Management
A major telecommunications provider deployed an Ihm Scada system to manage its network's operational status. The system allowed them to visualize traffic flow across the network, enabling quicker troubleshooting of any outages. After implementing the Ihm Scada solution, the company noticed a reduction in outage response time by 40%, significantly improving customer service and satisfaction.
Conclusion: A Vision for the Future with Ihm Scada
The strategic value of Ihm Scada systems cannot be overstated; they are instrumental in driving operational excellence and ensuring industries remain agile in a fast-evolving technological landscape. By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing education and training, organizations can maximize the potential of Ihm Scada systems to meet their operational goals effectively.
Ultimately, as industries face greater pressures for efficiency, safety, and sustainability, the role of Ihm Scada systems will become even more central to their operations. Forward-thinking organizations that invest in these systems will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of modern industrial landscapes and leverage their strategic advantages for ongoing success.